Last Updated on 8 April 2024
What’s better, IUD or pill? This is a question that I have been asked by my patients more times than I can count. This is quite understandable because choosing a suitable form of birth control can be a daunting task. With so many options available, it is essential to understand the differences between each method to make an informed decision. Two commonly used forms of contraception are intrauterine devices (IUDs) and birth control pills. Both options have their advantages and disadvantages, and what works for one person may not work for another. In this article, we will explore the key factors to consider when deciding between an IUD and a pill.
When it comes to birth control, effectiveness is a top priority. Nobody wants to take unnecessary risks when it comes to preventing unwanted pregnancies. Both IUDs and birth control pills are highly effective forms of contraception when used correctly. However, their effectiveness rates may vary, and it is essential to understand the pros and cons of each method.
In addition to effectiveness, it is also crucial to consider side effects, duration of use, and cost. Every person’s body is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. By understanding the differences between IUDs and birth control pills, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your needs and preferences.
What Are IUDs and Birth Control Pills?
IUDs and birth control pills are two popular methods of contraception. An intrauterine device, or IUD, is a small T-shaped device that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. It can be either hormonal or non-hormonal. On the other hand, birth control pills, also known as oral contraceptives, are taken daily and contain hormones that prevent pregnancy. Both methods alter the body’s hormonal balance to prevent ovulation and/or fertilization.
How Do IUDS And Birth Control Pills Work?
IUDs and birth control pills work in different ways to prevent pregnancy. Hormonal IUDs, such as Mirena or Kyleena, release a hormone called progestin, which thickens the cervical mucus and thins the lining of the uterus. This makes it more difficult for sperm to reach the egg and prevents the egg from implanting in the uterus. Copper IUDs, like ParaGard, do not contain hormones. Instead, they release copper, which creates a toxic environment for sperm, preventing fertilization.
Birth control pills, on the other hand, contain synthetic hormones, usually a combination of estrogen and progesterone. These hormones work together to prevent ovulation, which is the release of an egg from the ovaries. Additionally, they thicken the cervical mucus, making it harder for sperm to swim through the cervix and reach the egg. They also thin the uterus lining, making it less receptive to implantation. Understanding how each method works lets you decide which option is right for you.
Key Differences between IUDs and PILLs That You Need to Know
When it comes to deciding between an IUD and the pill, there are several key differences to consider. Firstly, the method of use is different. An IUD is a physical device inserted into the uterus, while the pill is taken orally. The type of IUD also varies, with hormonal and copper options available.
Another difference is the duration of use; an IUD can last for several years, and it is basically a set-it-and-forget-it option, while the pill needs to be taken daily. This can be a factor for those who prefer a long-term solution versus a daily routine.
Exploring the Types of IUDs and Pills
When it comes to IUDs, there are two main types to consider: hormonal and copper. Hormonal IUDs, such as Mirena and Kyleena, release progestin and are highly effective in preventing pregnancy. Copper IUDs, like ParaGard, do not contain hormones and work by creating an environment that is toxic to sperm.
When it comes to birth control pills, there are also different types to choose from. Combination pills contain both estrogen and progestin, while progestin-only pills contain only progestin. Combination pills are often used to reduce period pain, regulate menstrual cycles, and improve acne symptoms. Progestin-only pills are a good option for those who cannot take estrogen due to health reasons.
By exploring the different types of IUDs and pills, you can determine which option aligns with your individual needs and preferences.
Hormonal vs. Copper IUDs
One key difference between IUDs is the type of contraception they provide. Hormonal IUDs, as the name suggests, release hormones (progestin) into the uterus. These hormones thicken the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg. Hormonal IUDs also thin the lining of the uterus, which can result in lighter periods. In some cases, menstruation may stop altogether.
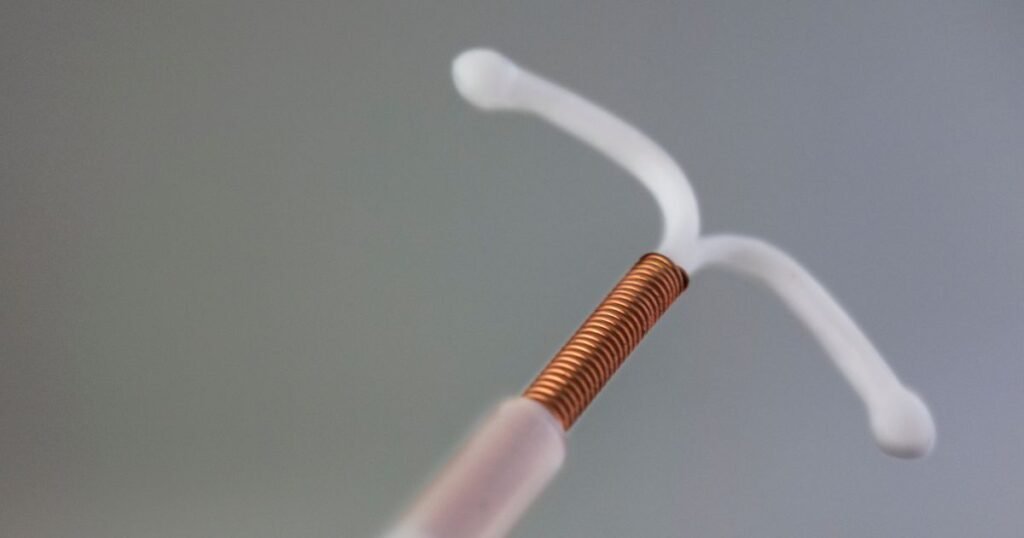
On the other hand, copper IUDs do not release hormones. They work by releasing copper into the uterus, which creates an environment that is toxic to sperm. Copper IUDs are a good option for individuals who prefer a non-hormonal method of contraception.
When deciding between hormonal and copper IUDs, it’s essential to consider your menstrual cycle. Hormonal IUDs may lead to lighter or no periods, which can be beneficial for those with heavy or painful periods. Copper IUDs, on the other hand, do not affect the menstrual cycle. By understanding the differences between hormonal and copper IUDs, you can make an informed decision about which option is right for you.
Combination Pills vs. Progestin-Only Pills
When it comes to birth control pills, there are two main types to consider: combination pills and progestin-only pills. Combination pills contain both estrogen and progestin, while progestin-only pills contain only progestin.
Combination pills are often prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce period pain, and improve acne symptoms. They work by preventing ovulation, thickening the cervical mucus, and thinning the lining of the uterus. These pills are highly effective when taken correctly.
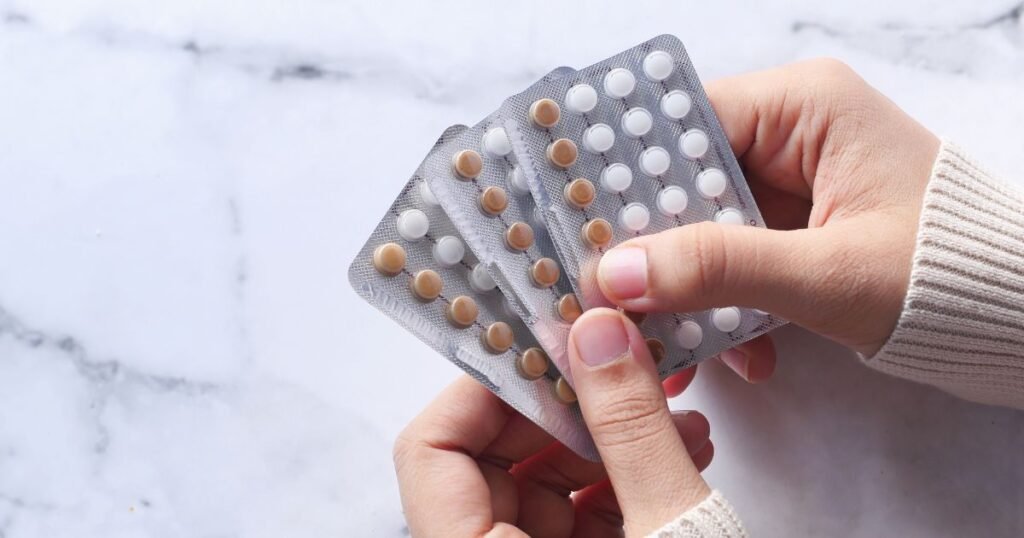
Progestin-only pills are a good option for individuals who cannot take estrogen due to health reasons, such as those with a history of blood clots or migraines. These pills work by thickening the cervical mucus and thinning the lining of the uterus, making it more difficult for sperm to reach the egg and preventing implantation.
When deciding between combination pills and progestin-only pills, it is essential to consider any health conditions or risk factors that may influence your choice. By understanding the differences between these pills, you can decide which option is right for you.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of IUDs vs. Pills
When evaluating the effectiveness of IUDs vs. pills, it is essential to consider both perfect use and typical use rates. Perfect use refers to using the method correctly every time, while typical use considers human error or inconsistent use.
Both IUDs and pills are highly effective forms of contraception when used correctly. IUDs have a slightly higher effectiveness rate than pills, with less room for error. However, both methods are highly effective when used consistently and correctly.
It is important to remember that no form of birth control is 100% effective, and there is always a small risk of pregnancy. Using the chosen method consistently and correctly can maximize its effectiveness and reduce the risk of unintended pregnancy.
what’s better iud or pill? For Preventing Pregnancy
Both IUDs and birth control pills are highly effective in preventing pregnancy when used correctly. However, the success rates of each method can vary. IUDs have a very high success rate in terms of perfect use. Hormonal IUDs are over 99% effective, while copper IUDs are over 99% effective as well. This means that fewer than 1 in 100 women will become pregnant during the first year of using an IUD.
Birth control pills also have a high success rate when used properly. Combination pills are over 99% effective, while progestin-only pills are around 99% effective. This means that fewer than 1 in 100 women will become pregnant during the first year of using the pill.
Factors That Influence Effectiveness of Contraceptives
While both IUDs and birth control pills are highly effective forms of contraception, there are certain factors that can influence their effectiveness. These factors may vary from person to person, including risk factors, menstrual irregularities, and heavier periods.
Certain risk factors, such as smoking or having a history of blood clots, can increase the risk of certain complications and may impact the effectiveness of hormonal birth control methods, including both IUDs and birth control pills. It is important to discuss these risk factors with your healthcare provider and determine the best method of contraception for your individual circumstances.
Side Effects and Health Considerations
When it comes to considering side effects and health considerations, it is important to understand that both IUDs and birth control pills may have potential side effects. These side effects can vary from person to person and may include cramping, insertion discomfort, breast tenderness, nausea, and changes in menstrual bleeding.
Common side effects of IUDs include cramping and discomfort during and after insertion, as well as irregular bleeding or spotting between periods. These side effects are usually temporary and resolve on their own.
Similarly, birth control pills can cause side effects such as breast tenderness, nausea, and changes in menstrual bleeding. These side effects are usually mild and improve over time.
It is important to discuss any potential side effects with your healthcare provider and determine the best method of contraception for your individual health considerations. By understanding the possible side effects, you can decide which option is right for you.
Common Side Effects of IUDs
Common side effects of IUDs may include cramping, insertion discomfort, and changes in menstrual bleeding patterns. These side effects are usually mild and temporary, and most people find that they resolve independently over time.
Cramping is a common side effect that can occur immediately after the insertion of an IUD. This is because the uterus may need time to adjust to the device’s presence. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate cramping.
Insertion discomfort is another common side effect that may occur during or after the insertion procedure. Some people may experience mild to moderate discomfort, while others may not feel any discomfort at all. This discomfort is usually temporary and should subside within a few days.
Changes in menstrual bleeding patterns are also common with IUD use. Some people may experience irregular bleeding or spotting between periods, while others may notice lighter or heavier periods. These changes are usually temporary and should normalize within a few months.
If you experience any side effects that are severe or persistent, it’s important to contact your healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance.
Potential Side Effects of Birth Control Pills
Birth control pills may have potential side effects, although many people tolerate them well. Some common side effects of birth control pills include breast tenderness, nausea, and changes in menstrual bleeding.
Breast tenderness is a relatively common side effect of birth control pills. This can cause discomfort or sensitivity in the breasts. In most cases, this side effect is temporary and resolves independently.
Nausea is another potential side effect of birth control pills. Some people may experience mild nausea, especially when starting a new pill. Taking the pill with food or at bedtime can help reduce the likelihood of experiencing nausea.
Changes in menstrual bleeding patterns are also common with birth control pill use. Some people may experience lighter or shorter periods, while others may experience spotting between periods. These changes are usually temporary and resolve within a few months of starting the pill.
It is important to remember that while serious side effects are rare, birth control pills can increase the risk of blood clots and high blood pressure in some individuals. It is important to discuss your individual risk factors with your healthcare provider to determine the best method of contraception for you.
Lifestyle Compatibility and Convenience
When it comes to lifestyle compatibility and convenience, it’s essential to consider factors such as daily routine, impact on the menstrual cycle, and the level of convenience each method provides.
Birth control pills require a daily routine of taking a pill at the same time each day. This can be convenient for some individuals with a structured schedule and can easily incorporate pill-taking into their daily routine. However, it can be challenging for those with irregular schedules or difficulty remembering to take a pill consistently.
IUDs, on the other hand, offer a long-term solution that does not require daily attention. Once inserted, an IUD can provide contraception for several years, depending on the type. This can be convenient for those who prefer a set-it-and-forget-it method of contraception.
Additionally, both birth control pills and IUDs can have an impact on the menstrual cycle. Some individuals may experience changes in their period, such as lighter or heavier bleeding, irregular bleeding, or spotting. By considering your lifestyle and personal preferences, you can determine which method of contraception is most compatible and convenient for you.
Impact on Menstrual Cycle and Symptoms
Both birth control pills and IUDs can have an impact on the menstrual cycle and associated symptoms.
Birth control pills can help regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce symptoms such as heavy bleeding, cramping, and irregular periods. Some individuals may also experience shorter and lighter periods or the ability to skip their period altogether while taking birth control pills. This can be beneficial for those who experience uncomfortable or inconvenient menstrual symptoms.
IUDs can also impact the menstrual cycle. Some individuals may experience irregular bleeding or spotting between periods, especially in the first few months after insertion. However, others may notice lighter or no periods at all. This can be a benefit for those with heavy or painful periods, as well as those who prefer a method that reduces menstrual symptoms.
By considering the impact on your menstrual cycle and associated symptoms, you can determine which method of contraception is most suitable for your individual needs.
Cost Analysis and Insurance Covrage
When considering the cost of contraception, it’s important to evaluate both upfront costs and long-term expenses. Additionally, understanding insurance coverage and navigating policies can help make the right decision.
The cost of birth control pills varies depending on insurance coverage, with some generic brands being available for less than $10 per month. However, name-brand pills can cost up to $50 per month. It’s important to check your insurance policy to determine the coverage for birth control pills.
For IUDs, the cost can range from free to around $1,000, depending on insurance coverage. This cost includes the device and the insertion procedure. Some insurance plans cover the full cost, while others may require a copay or deductible.
Navigating insurance policies can be challenging when it comes to contraception. It is important to consult with your insurance provider and healthcare provider to determine the coverage for your chosen method and any potential costs you may incur.
Upfront Costs vs. Long-Term Expenses for contraception
When considering the cost of contraception, it’s important to evaluate both upfront costs and long-term expenses. While birth control pills may have a lower upfront cost, they require ongoing monthly purchases, which can add up over time. The cost of birth control pills varies depending on insurance coverage, with some generic brands being available for less than $10 per month. However, name-brand pills can cost up to $50 per month.
IUDs, on the other hand, have a higher upfront cost but provide contraception for several years, with no additional monthly expenses. The cost of an IUD can range from free to around $1,000, depending on insurance coverage. While the upfront cost may be higher, the long-term expenses can be significantly lower compared to birth control pills.
By evaluating both upfront costs and long-term, you can make an informed decision about which method of contraception aligns with your financial considerations.
Navigating Insurance Policies
Navigating insurance policies when it comes to contraception can be challenging. It’s important to understand your insurance coverage and any potential out-of-pocket expenses you may incur.
Most insurance plans cover some form of birth control, including birth control pills and IUDs. However, the level of coverage can vary depending on the specific insurance plan and the type of method chosen. It’s important to consult with your insurance provider to determine the coverage for your chosen method and any potential costs you may incur.
In some cases, insurance plans may require a copay or deductible for contraception. However, the Affordable Care Act mandates coverage for birth control as part of preventive care, so many insurance plans cover birth control at no cost to the individual.
Additionally, clinics like Planned Parenthood offer sliding fee scales for patients who do not have insurance to ensure everyone has access to birth control that meets their family planning needs. By understanding your insurance coverage and navigating policies, you can make an informed decision about which method of contraception aligns with your financial considerations.
Making an Informed Decision
When it comes to choosing between an IUD and the pill, it’s important to make an informed decision based on your individual needs, preferences, and health considerations.
Consultation with healthcare providers is crucial in the decision-making process. They can provide valuable information, answer any questions or concerns you may have, and help guide you towards the most suitable method of contraception for you.
Factors to consider when making an informed decision include your medical history, lifestyle, insurance coverage, and personal preferences. By weighing these factors and discussing them with your healthcare provider, you can make a decision that aligns with your individual needs and ensures effective contraception.
Consultation with healthcare providers is an essential step in making an informed decision about contraception. They have the expertise and knowledge to guide you towards the most suitable method of contraception for your individual needs.
During a consultation, healthcare providers can discuss your medical history, lifestyle, and personal preferences to determine the best method of contraception. They can provide valuable information about the effectiveness, potential side effects, and usage instructions for each method.
Additionally, they can address any concerns or questions you may have and provide guidance on navigating insurance coverage and accessing affordable contraception. By working with your healthcare provider, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your personal health considerations and ensures effective contraception.
Considering your personal health and any existing health conditions is crucial in making an informed decision about contraception. Certain health conditions or risk factors may influence the suitability of certain methods. It’s important to discuss your personal health with your healthcare provider to ensure that the chosen method is safe and effective for you.
In conclusion, deciding between IUDs and birth control pills depends on your lifestyle, preferences, and health considerations. Understanding the differences in effectiveness, side effects, convenience, cost, and impact on your body can help you make an informed choice. Consultation with healthcare providers is crucial in determining the best option for you. Consider factors like daily routine, long-term solutions, menstrual cycle changes, and insurance coverage before deciding. Both methods have their pros and cons, so it’s essential to prioritize what aligns best with your individual needs and goals. There are other natural ways to prevent pregnancy, such as tracking your ovulation date. Ultimately, the right choice is the one that suits you best.









